GNOME is getting better! More and more useful tools are available to configure the desktop behavior and appearance.
For those running Linux with Gnome Desktop, such as Ubuntu, Fedora, CentOS, Debian, and Arch Linux, the default ‘Settings’ tool is great but not enough.
The default “Gnome Control Center” provides options to configure basic settings for Wi-Fi, network, bluetooth, privacy, background, power, sound, and peripherals. However, it lacks ability to change themes, text fonts, extensions, and other hidden settings.
So I’m here to show you 6 more other configuration tools that can help you to have better experience in Linux with GNOME.
1. Gnome Tweaks
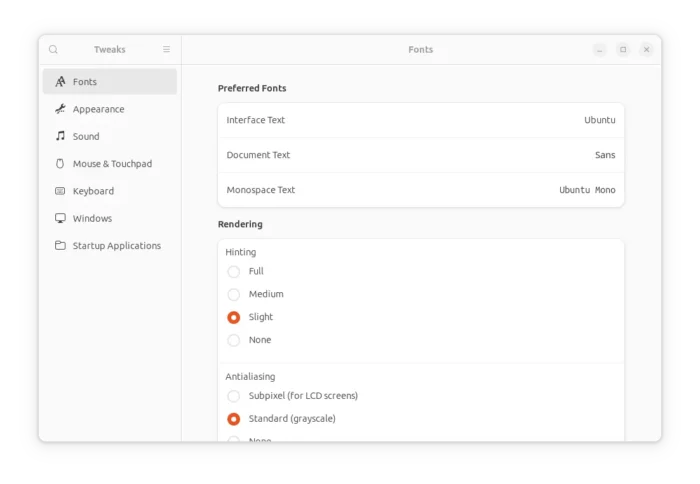
GNOME Tweaks is one of the must have apps for GNOME Desktop, that is even pre-installed in some Linux distributions, e.g., Debian 11.
What can Gnome Tweaks do:
As the name indicates, it’s a tool to tweak Gnome desktop. With it, you can do:
- Change Themes for legacy GTK3 apps, mouse pointer, app icons, Gnome Shell (the desktop), and sound.
Manage Gnome Shell extensions.- Configure system fonts, and adjust scaling factor.
- Add/remove title bar buttons (minimize, maximize, close), and move the position
- Manage startup applications.
Show or hide battery percentageShow/hide weekday, date, seconds in clock, and week number in calendar- Toggle
animations, automatic suspend when lid closed. - Some more keyboard & mouse settings.
work-spaceswindow actions, settings.
Some are either moved to GNOME Control Center (the default settings), or split into another tool. So, they are deleted via strikethrough in the list above.
How to Install Gnome Tweaks:
As I mentioned, the tool is available out-of-the-box in some Linux. Just press Super (Windows logo) key to trigger overview screen, then try to search and open it in the overview screen.
If not exist, you may search for and install it either in “Ubuntu Software” (or App Center in 23.10/24.04), “Gnome Software”, or via your system package manager, such as Pamac – Manjaro’s package manager.
2. Dconf Editor
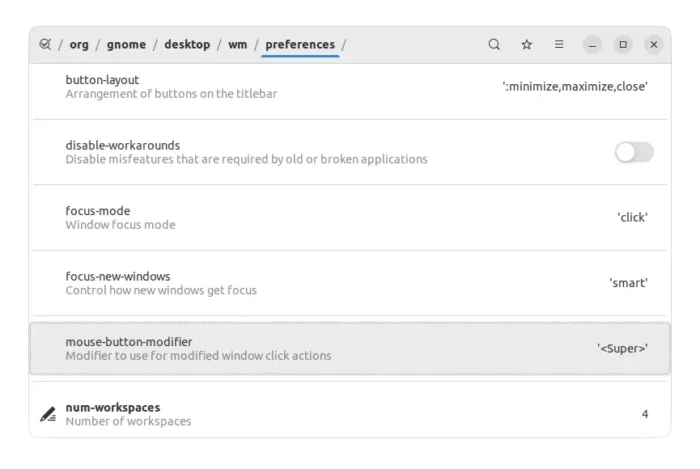
This is an advanced tool that includes the most configurations you can do for your system. And, not only for GNOME, this tool also works for MATE, XFCE, Cinnamon desktops.
Dconf Editor is a graphical interface for gsettings and dconf command line tools. It has so many configuration options, that it’s not even recommended for beginners in case of breaking things down. And some keys need different user privilege to make changes.
What Dconf Editor can do:
- Configure all extension settings, e.g., dash to dock (Ubuntu Dock).
- Tweak login screen, e.g., hide user-list, disable shutdown, etc., with gdm user privilege.
- Change Gnome Shell keybindings.
- And numerous other hidden settings, for either Gnome Desktop or Applications.
How to Install Dconf Editor in Linux:
Same to Gnome Tweaks, user can simply search for and install Dconf Editor from Ubuntu Software (App Center) / Gnome Software or your system package manager.
3. GNOME Extensions App & Extension Manager
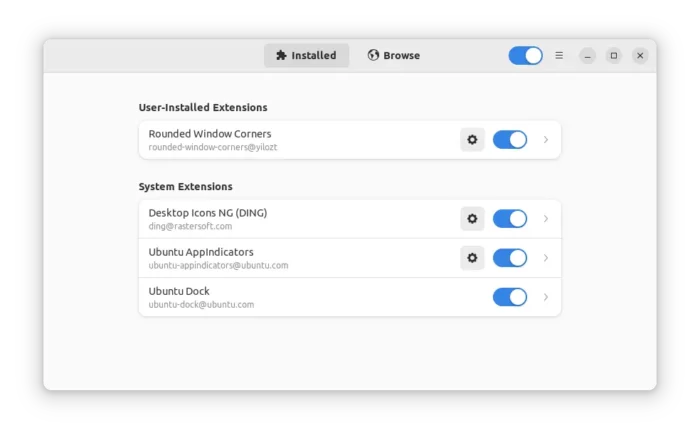
This is definitely 2 apps, but do same things for managing extensions.
Since Gnome 40, defaults in Fedora 34+ and Ubuntu 21.10+, Gnome Tweaks removes the function to manage extensions. Instead, Gnome Extensions App and Extension Manager are there to do the job.
Gnome has tons of extensions developed by either the official team or third-party contributors. With them, you can customize the desktop and achieve the functions of what you want. And, here are the tools to manage them.
Gnome Extensions App / Extension Manager features:
With the tools, you can do:
- Turn on/off extensions, for either global or single.
- Open extension config dialog if any.
- Remove extension, get extension description and other info.
- And indicate extension updates.
Extension Manager also has the ability to search & install Gnome extensions.
How to Install the Apps:
Gnome Extensions app is available to install in most Linux’s system repositories. Just search for and install it via your system package manager (e.g., Ubuntu Software, App Center, Gnome Software, pamac).
The Extensions Manager is also available in Ubuntu 22.04+, Debian 12, Arch Linux repositories. So, you can also install it via your system package manager. Other Linux can get it via Flatpak package.
4. Grub Customizer
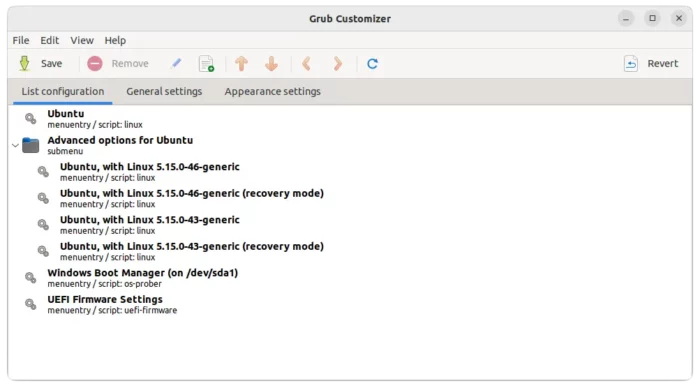
This tool is not only for Gnome, but for all Linux uses Grub to handle the startup boot-menu. It a free and open-source tool to configure the boot screen appearances without struggling with Linux commands.
With it, you can do:
- add, move, remove or edit boot screen menu entries.
- re-install Grub into Microsoft MBR.
- set default OS to boot.
- show/hide boot-menu, add kernel parameters.
- change boot screen appearances, including font, background, screen resolution and theme.
How to Install Grub Customizer in Linux:
The software is popular and available in official Linux repositories. So you can install it either from the Software Manager (App Center), or run command in terminal:
- For Ubuntu, Debian, Linux Mint run:
sudo apt install grub-customizer
- And for Fedora based systems, use command:
sudo dnf install grub-customizer
- Arch Linux run this command in terminal to get it:
sudo pacman -S grub-customizer
User can’t install Grub-Customizer in Manjaro Linux due to conflict to system default Grub package.
Grub-Customizer is NOT available in Ubuntu (since 22.04) repository due to scripting issue.
The software developer fixed the issue and published the package into official PPA. User may open terminal and run commands below one by one to get it:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:danielrichter2007/grub-customizer
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install grub-customizer
5. GDM Settings
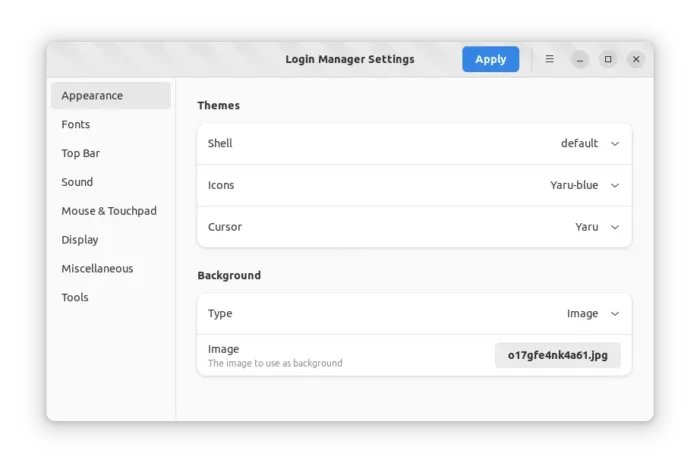
Login Manager Settings (aka GDM Settings) is a new free open-source tool for configuring Gnome Login screen. With it, you can do:
- Change login screen themes.
- Set background wallpaper or color for login screen.
- Change login font, scaling factor.
- Enable night light for login screen.
- Disable user list.
- Change logo and set welcome message, etc.
How to Get GDM Settings
The app provides non-install AppImage, available to download in the project releases page:
Once you get the package, right-click on it and go to “Properties -> Permissions”, then add executable permission via ‘allow executing file as program‘ checkbox. Finally, click run AppImage to launch the tool.
It’s also available to install as universal Flatpak package. Run the bottom command in that page after following the setup guide.
6. Just Perfection
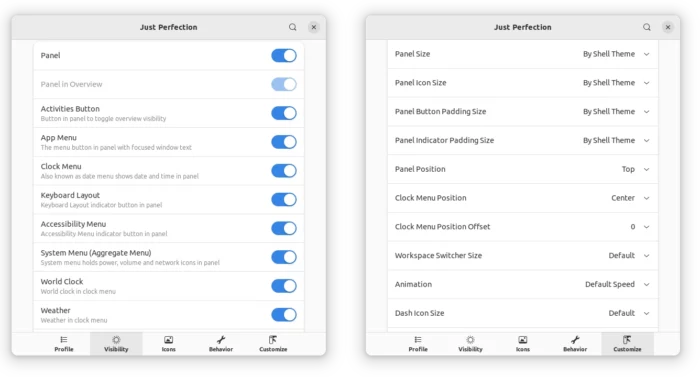
This is an extension that provides lots of options to configure Gnome behavior and disable UI elements.
With it, user can configure:
- Show/hide top-panel, left/bottom dock, activities, clock menu, system tray menu, search box, OSD.
- Select login to blank desktop or overview.
- Change panel size, panel icon size/padding.
- Panel position to bottom.
- Clock position to right/left.
- Disable or change animation speed.
- Notification position.
- Alt-Tab window preview size.
How to install Just Perfection
Simply go to the link page below, and turn on the slider icon will install the extension for your system:
Ubuntu needs to run sudo apt install chrome-gnome-shell to install the agent package.
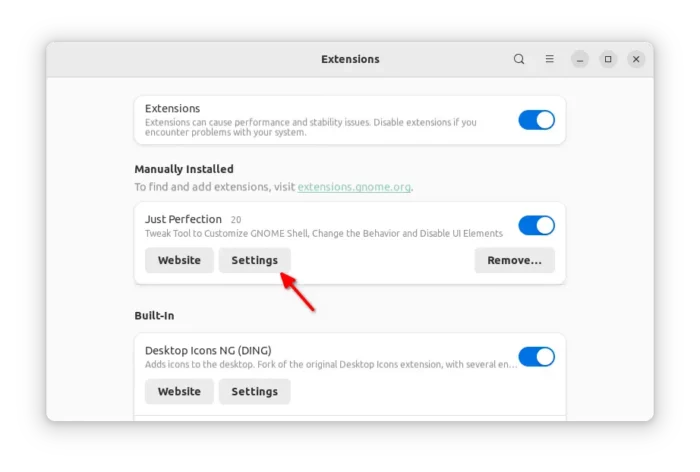
Or, use the “Extension Manager” that introduced above to search for and install the extension. To open config dialog, use either ‘Gnome Extensions App’ or ‘Extensions Manager’:
Summary:
Along with the default Settings tool, aka Gnome Control Center, there are some other useful tools to configure your desktop. They are “Gnome Tweaks”, “Dconf Editor”, “Gnome Extensions App/Extension Manager”, “GDM Settings”, and “Just Perfection” extension.















Recent Comments