This simple tutorial shows how to enable Wi-Fi hotspot in most Linux desktop, including Ubuntu, Fedora, KUbuntu, Linux Lite, Manjaro, and more.
Some of our dear readers said this tutorial does not work in their systems. So, I’m here to re-write it with options for most popular Linux Distributions.
Requirements
First of all, you have to make sure that:
- Your PC/laptop has connected to internet.
- A Wi-Fi adapter is free for access point.
Meaning you need 2 network cards: one connected to internet (usually wired network), and a wireless card to work as access point.
Option 1: Enable Wi-Fi HotSpot in Ubuntu, Fedora, other Linux with GNOME:
This is for GNOME, the default desktop in Ubuntu, Fedora Workstation and optional in Debian, Manjaro, Arch, Rocky Linux.
1. Firstly, open Gnome-control-center (aka Settings) from upper right corner system menu.
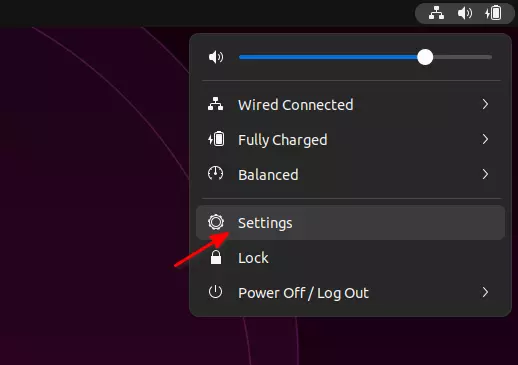
2. In the first Wi-Fi page, make sure you have turned on the switch in header bar. Then click on the tree dots ‘⁝‘ icon, and select ‘Turn on Wi-Fi HotSpot‘ menu option.
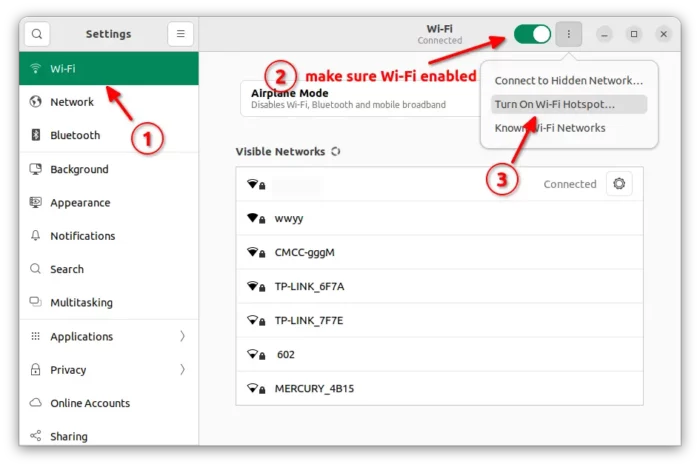
3. In the next pop-up dialog, set the password used for access this hostspot.
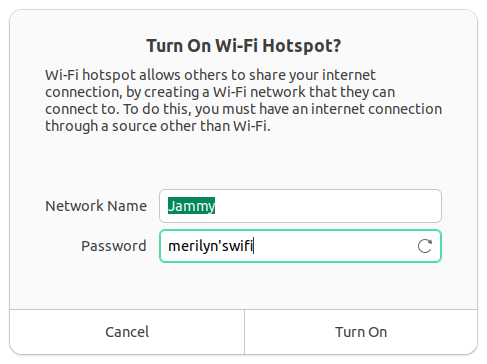
Once you click ‘Turn on’, the Wi-Fi settings page should display QR code that mobile device can scan to connect. As well, it displays the network name, security type (WPA & WPA2 Personal by default) and the password.
Option 2: Enable Wifi hotspot in KDE Plasma (KUbuntu, Ubuntu Studio, etc)
This is for the KDE Plasma desktop, which is default in KUbuntu, Ubuntu Studio, KDE neon, and optional in other Linux including Arch, Debian, Fedora, Manjaro and more.
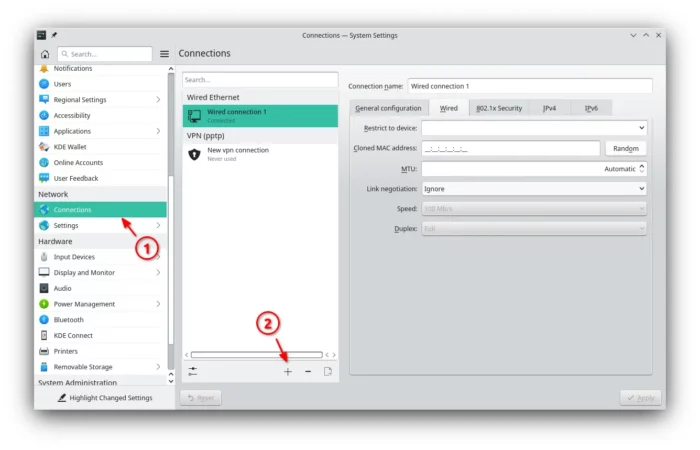
1. First, search for and open “System Settings” from start menu. When it opens, navigate to “Network -> Connections” from left. Then, click the bottom “+” to create a new network.
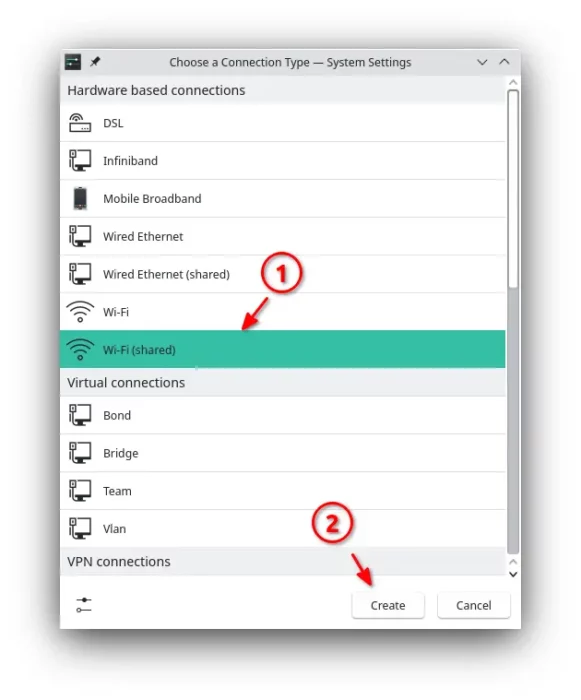
2. In the pop-up dialog, select “Wi-Fi (shared)” and then click on the “Create” button.
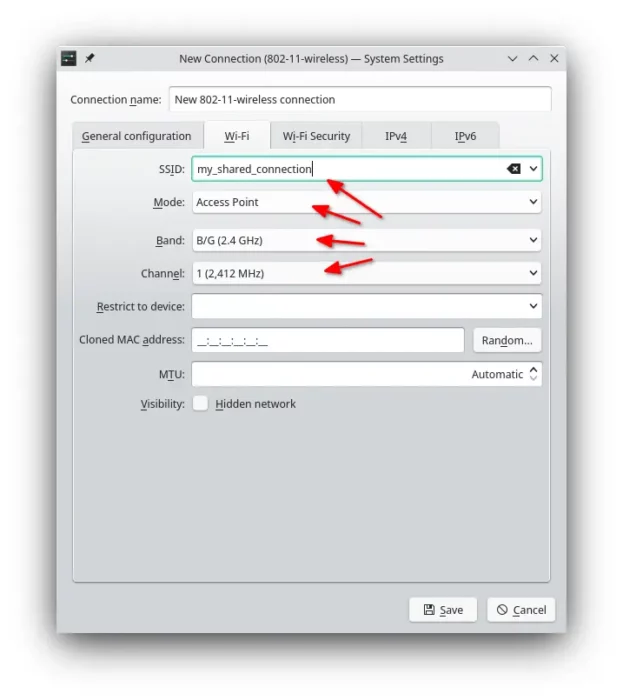
3. Finally, it opens the dialog for setting the following options:
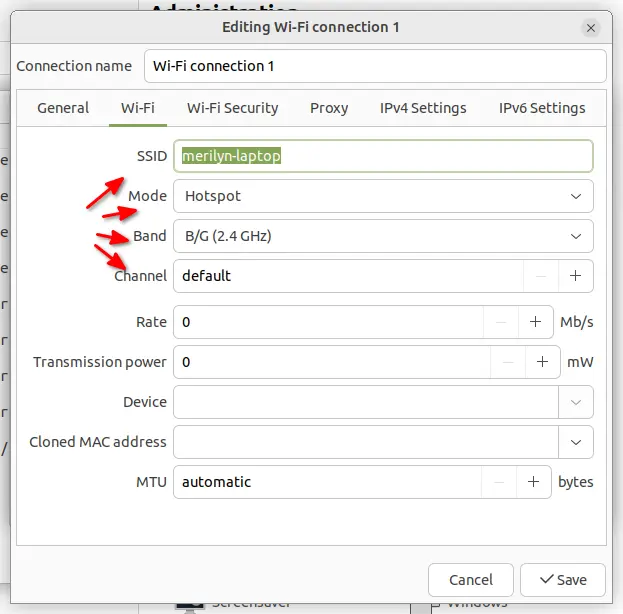
- SSID – the wireless network name, when you try to connect via mobile phone.
- Infrastructure or access point. (see the difference)
- 2.4G or 5G (make sure your wireless card support it)
- Channel – optional.
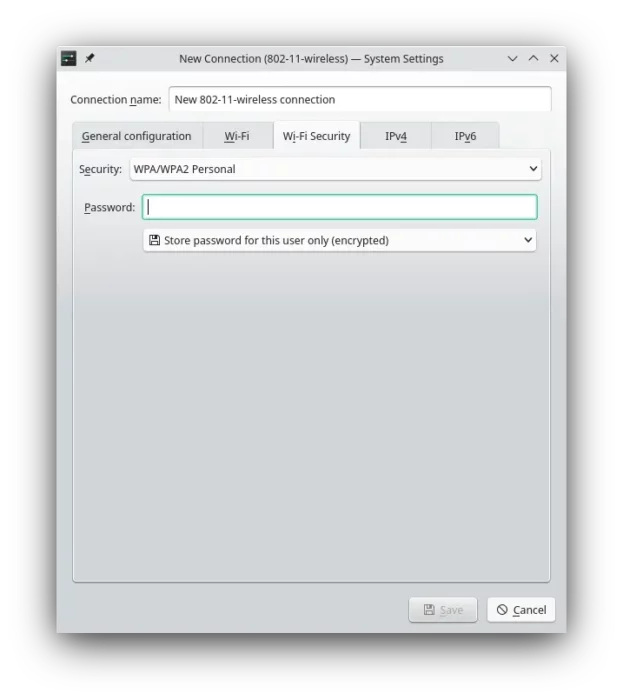
And, switch to “Wi-Fi Security” tab to set a password for this network. Usually, we use WPA/WPA2 Personal security type.
After clicked “Save” button, go to system tray wifi applet, and select connect to the network (see “Connection name” in last screenshot) you just created! Finally, try connection the SSID in your mobile phone!
Option 3: For Linux Mint, Linux Lite, Ubuntu MATE, and other Linux
I’ve also tried to achieve this in a few other Linux Distros, including LUbuntu, Ubuntu MATE, Linux Mint, XUbuntu, Zorin OS and Pop! OS. They work in similar way.
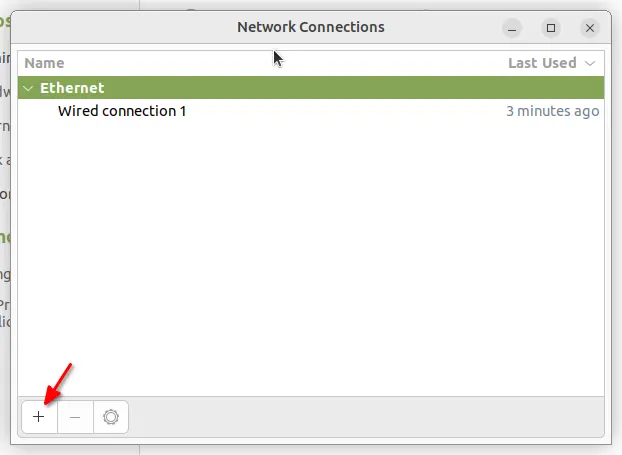
1. Open “Advanced Network Configuration”
First, open the “Advanced Network Configuration” utility, either from start menu or your system control center.
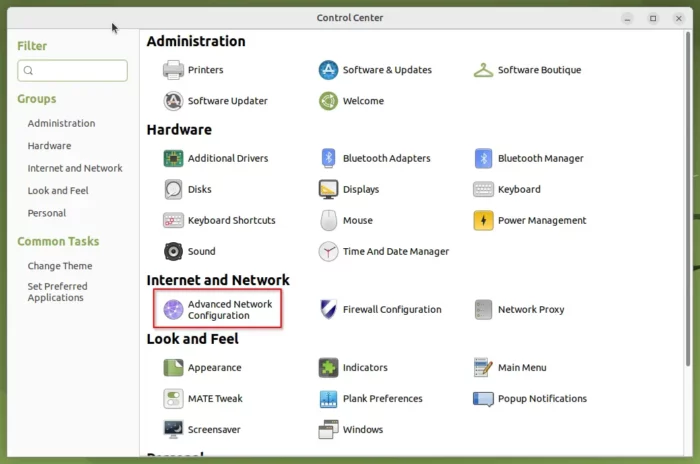
In case you can’t find the tool from system menu, open “terminal” and run command to start the utility:
nm-connection-editor
It brings up the network editing dialog for most GTK-based desktops. Meaning you can also use the command in Ubuntu, Fedora, etc.
Ubuntu, Fedora and other Linux with GNOME, can use this tool to edit the HotSpot created by Gnome Control Center.
2. Create a Wi-Fi network and set as hotspot
In the previous dialog, click bottom-left “+” to create a new work. Then, choose “Wi-Fi” in pop-up dialog.
It finally open the dialog for setting SSID, mode, 2.4G or 5G, Wi-Fi channel and so forth.
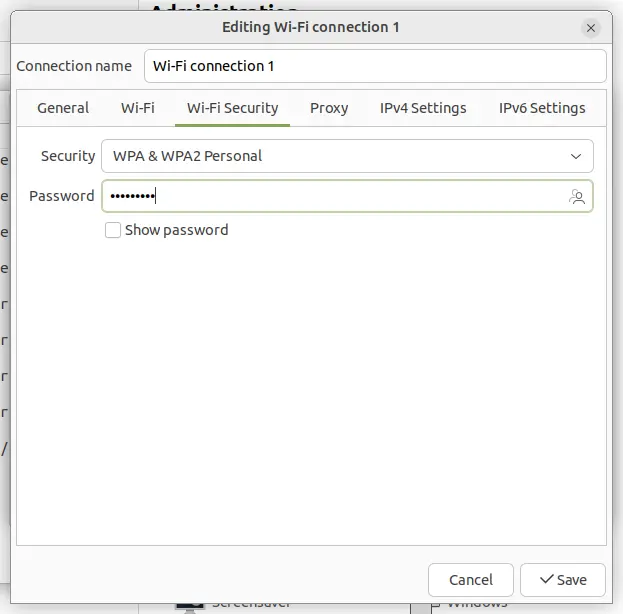
Also, in the “Wi-Fi Security” tab, set a password in WPA/WPA2 personal or other type as you prefer. Other settings are optional, though you may change them accordingly.
After saved the network, go to system tray Wi-Fi indicator applet and select connect to the ‘Connection name’ you just created. Finally, try connecting to this access point using your mobile phone.
Option 4: Create Wi-Fi hotspot from Command Line
For those familiar with Linux commands, the single command below may help creating wifi hotspot in Linux:
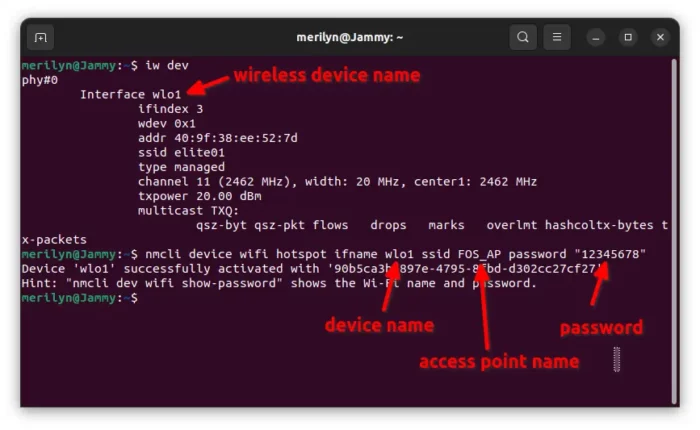
nmcli device wifi hotspot ifname DEVICE_NAME ssid AP_NAME password "PASSWORD"
In the command, you need to replace DEVICE_NAME with your Wi-Fi device name, and set custom AP_NAME and PASSWORD as prefer.
Once created successfully, try connect to the AP_NAME network in your mobile device and use the password you set to authenticate.
If you don’t know your wireless device name, run command:
iw dev
NOTE: The command works on my Ubuntu Desktop, but not tested in Server edition. If theiwtool is not available, run command:sudo apt install iwFor Ubuntu Server, you may also need to runsudo apt install network-managerto get thenmclicommand line tool.
















Recent Comments