Debian uses Firefox ESR, the Extended Support Release, as its default web browser. It mainly focuses on crash fixes, security fixes and policy updates, while receiving major updates with new features every 42 weeks.
It’s great for school or enterprise use. However, for personal computers or those prefer latest features, Mozilla provides the “Rapid release” channel with updates every month!
And, here you can install the latest Firefox ‘Rapid release’ in Debian 11/12 via 4 different ways:
- New apt repository
- Firefox Flatpak package.
- Firefox SNAP package.
- Linux portable tarball.
To focus on stability and easy to follow, I removed the install options from Debian Unstable and Ubuntu repositories. And, all the 3 ways are provided by Mozilla Team. Also, they will NOT affect the existing Firefox ESR in your system. Choose any one that you prefer!!
(New) Method 1: Install & Keep Firefox updated via official repository:
Since Firefox 122.0, Mozilla Team announced new official .deb package through its apt repository.
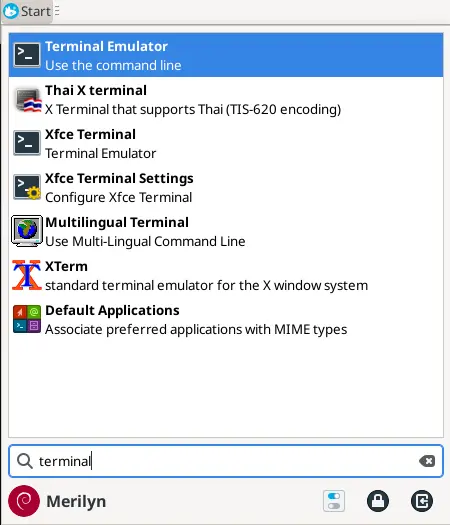
First, search for and launch a terminal window from either start menu or ‘Activities’ overview depends on your desktop environment.
Then, you can follow the steps below one by one to add the official Mozilla repository and install Firefox from it.
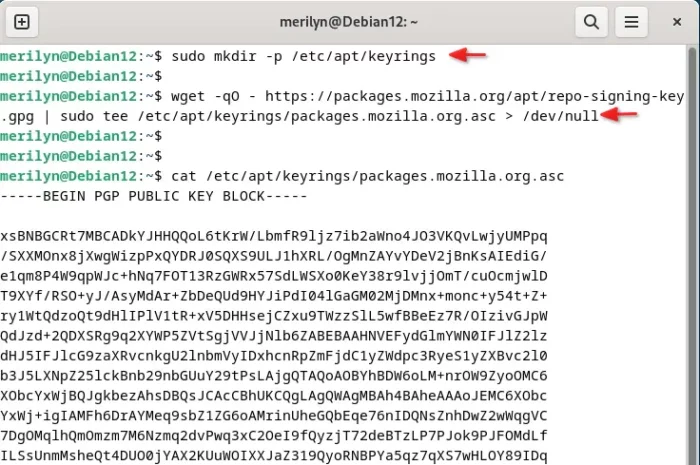
1. First, run command to make sure you have /etc/apt/keyrings directory for saving third-party repository keys.
sudo mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings
2. Then, run command to download the key file and save it to that directory:
wget -qO - https://packages.mozilla.org/apt/repo-signing-key.gpg | sudo tee /etc/apt/keyrings/packages.mozilla.org.asc > /dev/null
After that, you can run cat /etc/apt/keyrings/packages.mozilla.org.asc to print the key file to verify.
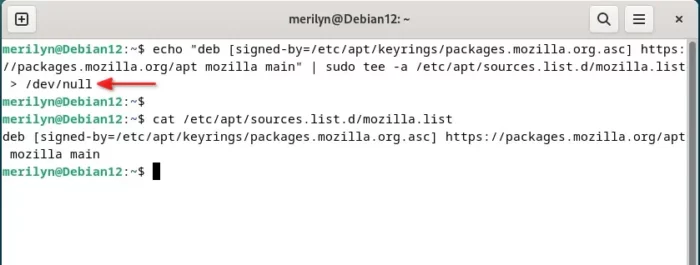
3. Next, run command to add the new Mozilla repository.
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/packages.mozilla.org.asc] https://packages.mozilla.org/apt mozilla main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mozilla.list > /dev/null
The command will create the mozilla.list file, and write the single line context (under quotes) into it. To verify the file, run cat /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mozilla.list to print it in terminal.
4. After installing the key and Mozilla repository, refresh system package cache via command:
sudo apt update
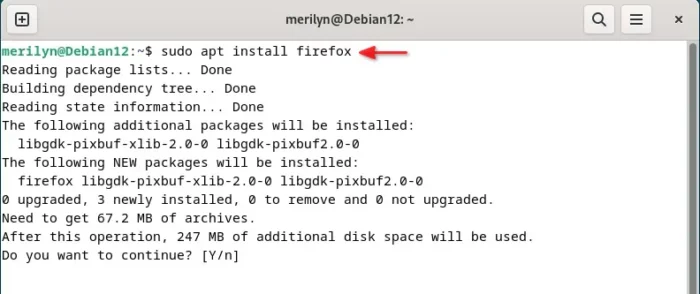
5. Finally, install the latest Firefox stable from that repository:
sudo apt install firefox
Tips: the repository also containsfirefox-beta,firefox-nightly, andfirefox-deveditionfor choices.
Method 2: Install Firefox via Portable tarball:
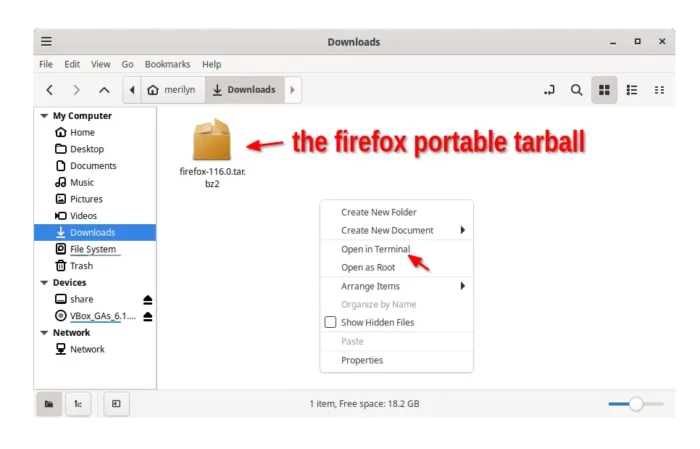
1. Download the tarball. Mozilla offers portable tarball packages for Linux 64-bit and 32-bit available to download via the link below:
2. After downloaded the package, open your Downloads folder. Then, right-click on blank area and select “Open in Terminal” (or “Open Terminal Here”).
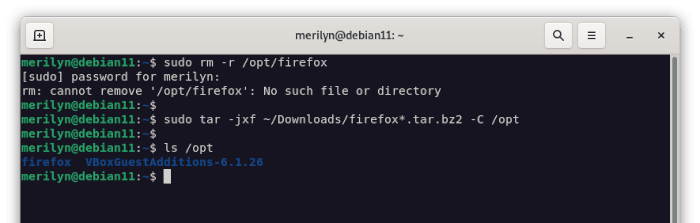
3. In the pop-up terminal windows, run following commands one by one to install (extract) to /opt directory:
- First, run command to remove ‘
/opt/firefox‘ directory, in case you have an old version of portable package installed.sudo rm -r /opt/firefox
- Then, extract the downloaded tarball from Downloads folder into ‘
/opt/‘ directory:sudo tar -jxf ~/Downloads/firefox-*.tar.bz2 -C /opt/
4. Finally, create an app shortcut by running the commands below one by one in terminal.
- First, create local app shortcut directory in case it does not exist:
mkdir -p ~/.local/share/applications
- Create, and edit a shortcut file using
nanocommand line text editor.nano ~/.local/share/applications/firefox.desktop
Then copy and paste the lines below into file (the terminal window):
[Desktop Entry]
Name=Firefox Stable
Comment=Web Browser
Exec=/opt/firefox/firefox %u
Terminal=false
Type=Application
Icon=/opt/firefox/browser/chrome/icons/default/default128.png
Categories=Network;WebBrowser;
MimeType=text/html;text/xml;application/xhtml+xml;application/xml;application/vnd.mozilla.xul+xml;application/rss+xml;application/rdf+xml;image/gif;image/jpeg;image/png;x-scheme-handler/http;x-scheme-handler/https;
StartupNotify=true
Actions=Private;
[Desktop Action Private]
Exec=/opt/firefox/firefox --private-window %u
Name=Open in private mode
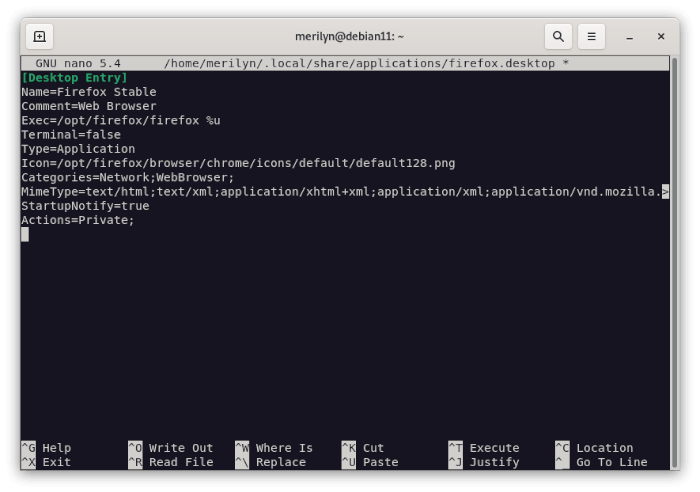
After that, press Ctrl+X, type y and hit Enter to save the file. Finally, search for and launch Firefox from start menu or ‘Activities’ overview (log out and back in if icon not visible).
Method 3: Install Firefox in Debian via Flatpak:
The Flatpak is an universal package format works in most Linux systems. It runs in sandbox with a separate daemon.
Firefox Flatpak supports only x86_64 (64-bit) PC/laptop.
1. Firstly, open terminal either from start/application menu, or by searching from ‘Activities’ overview depends on your Desktop environment.
2. Then, install Flatpak daemon package by running the command below in terminal:
sudo apt install flatpak
Type user password (no asterisk feedback) when it asks and hit Enter
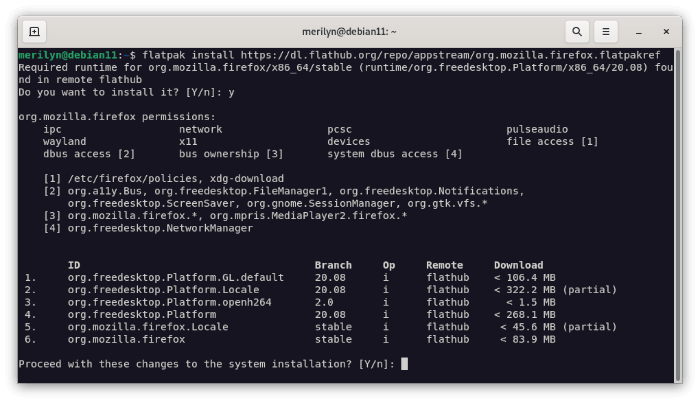
3. Finally, Install Firefox as Flatpak. To do so, copy and paste the command below into terminal and run to install the package as well as run-time libraries:
flatpak install https://dl.flathub.org/repo/appstream/org.mozilla.firefox.flatpakref
NOTE: First time installing a Flatpak package may also have hundred MB of downloads!
After installation, search for and launch Firefox from start menu or ‘Activities’ overview depends on your desktop environment (log out and back in may be required)!
In addition, when a new release is out. You may run the command below to update the Firefox Flatpak package:
flatpak update org.mozilla.firefox
Method 4: Install Firefox via SNAP:
The Mozilla team also provide Firefox package as the Linux universal SNAP.
As competitor to Flatpak, the SNAP also runs in sandbox, receives updates automatically, and takes more disk spaces! And snap is developed by Canonical, the company behind Ubuntu.
Firefox Snap package so far supports both x86_64, and arm64/armhf CPU architecture types. And, it updates automatically once new release is out.
- Firstly, open terminal and run command to install the SNAP daemon:
sudo apt install snapd
- Next, enable and start snapd daemon via commands:
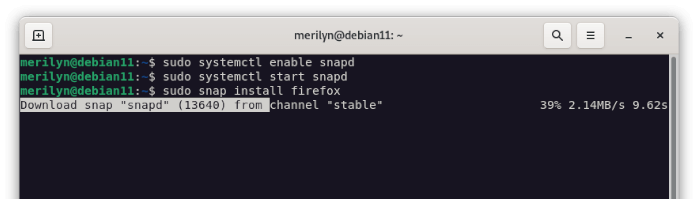
sudo systemctl enable snapd
sudo systemctl start snapd
- Finally, install Firefox as snap via command:
sudo snap install firefox
Like normal apps, you may search for and open Firefox snap from start menu. Though you’ll see more than one app icons if ESR is still exist.
Uninstall
Depends on which package you installed, select one of the commands below to remove the Firefox package in Debian:
- To remove Firefox
.debpackage, run command in terminal:sudo apt remove --autoremove firefox
Also, delete the Mozilla repository by running command:
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mozilla.list
Finally, run
sudo apt updateto refresh package cache. - To remove the Firefox Flatpak package, open terminal and run command:
flatpak uninstall --delete-data org.mozilla.firefox
Also run
flatpak uninstall --unusedto remove unused run-time libraries. - And, to remove Firefox installed via portable tarball. Just open terminal and run 2 commands to remove all the installed files:
sudo rm -r /opt/firefox rm ~/.local/share/applications/firefox.desktop
- For the snap package, run the command below to remove it:
sudo snap remove --purge firefox
If you don’t have any other Snap apps, you may also remove the daemon to free up disk space:
sudo apt remove --autoremove snapd