This is a beginner’s guide shows how to scan for wireless access points in Linux from command line.
NetworkManager has a built-in command-line interface called nmcli. With nmcli, you can create, display, edit, delete, activate, and deactivate network connections, as well as control and display network device status.
Supported Linux systems:
As the command line interface for NetworkManager, it should work on most Linux systems including Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora, and more.
Command to list wireless access points:
To scan for Wi-Fi access points, simply open terminal and run command:
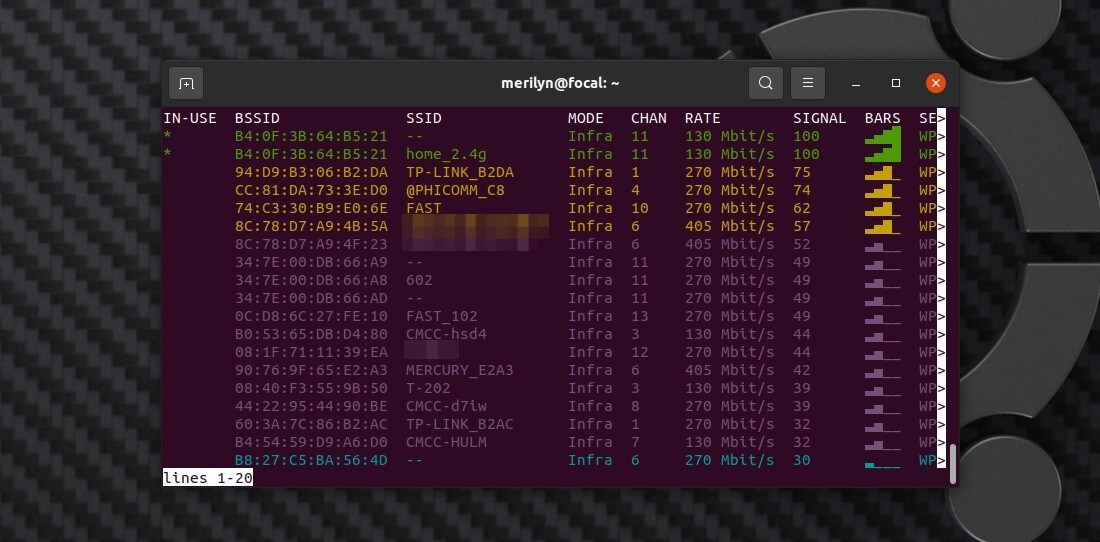
nmcli device wifi list
It will output a list of APs with information including BSSID, SSID, MODE, CHANNEL, SIGNAL, and more. Just as the top feature image shows.
Connect to a Wi-Fi AP via Linux command:
Simply run the command below in terminal will connect to a specified Wifi AP:
nmcli --ask device wifi connect "SSID_HERE"
with --ask flag, it asks for password before connection.
You can also type the password within the command, so it will be:
nmcli device wifi connect "SSID_HERE" password "PASSWORD_HERE"
And it will prompt that your Wi-Fi device activated successfully once connected.
Other nmcli commands:
The powerful command line tool can do many other useful things including:
- Toggle on or off networking via command:
nmcli networking on
nmcli networking off
- Enable or disable wifi via command:
nmcli radio wifi on
nmcli radio wifi off
- Reload connection profiles via command:
nmcli connection reload
It can also tell the current Wi-Fi connection password along with a QR code for sharing with friends.
For more about the tool, run man nmcli in terminal and enjoy!