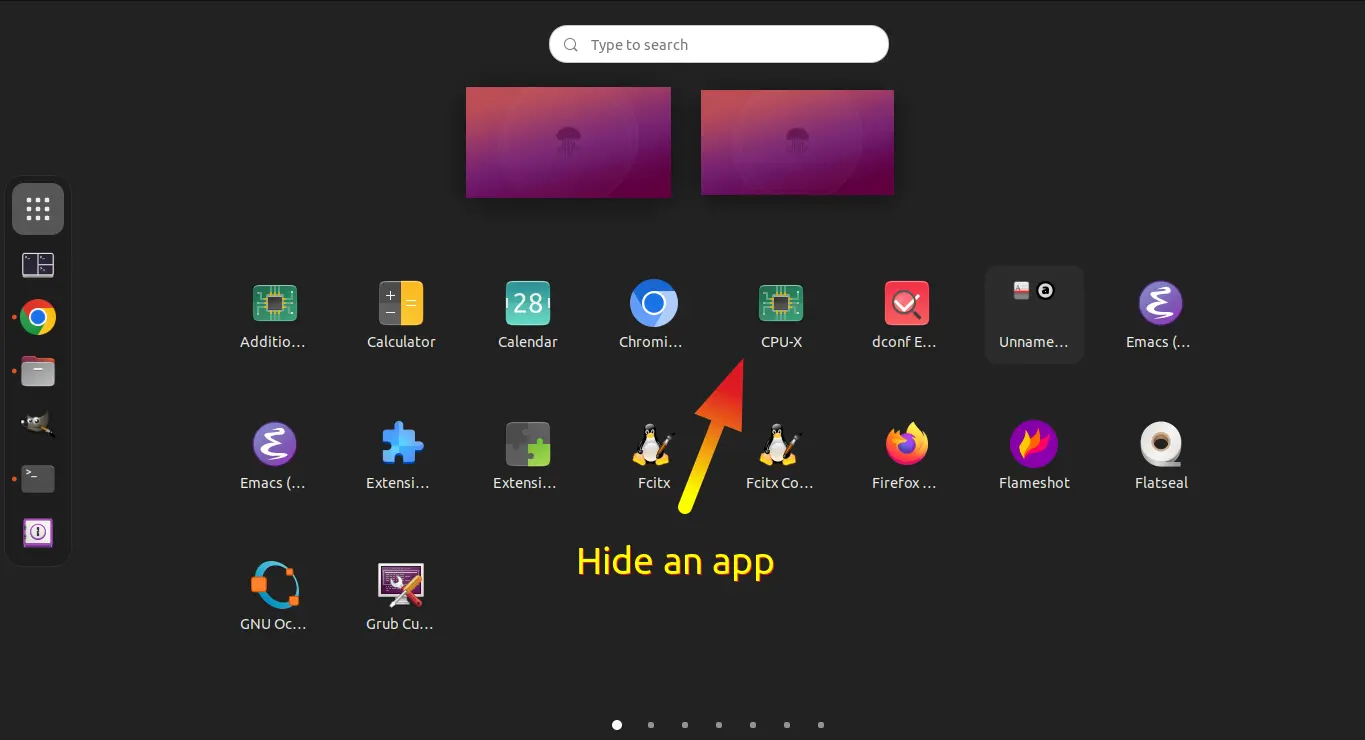
Want to hide your application, so it’s invisible in system app launcher and search result? This tutorial is going to show you how in 2 ways!
Method 1: Manually Edit The Shortcut File
Most Linux uses config file with .desktop extension to control application shortcut. By easily adding a rule into the .desktop file can hide the corresponding app shortcut.
Not only for Ubuntu & Fedora, this step works in most Linux!
1. First, open file manager and navigate to Other Locations ‘computer (or file system) > usr > share > applications‘. There, you’ll find the most .desktop app shortcut files on your system.
Just open another file manager window, press Ctrl+H to view hidden folders, then navigate to ‘.local > share > applications‘. Finally, drag and drop your desired apps’ shortcut files from ‘/usr/share/applications’ to ‘.local/share/applications’.
NOTE: For Flatpak applications, the .desktop files are stored under “/var/lib/flatpak/app/app_name_here/current/active/export/share/applications/”. You can either edit the file directly (need root permission), or drag and drop file into “~/.local/share/flatpak/” with same app path.
2. Now, right-click on the .desktop file and open in text editor.
You may skip step 1, and right-click on blank area of ‘/usr/share/applications’ folder and select “Open in Terminal”. Finally, run command below in terminal to edit the file via root permission: sudo nano file_name_here.desktop
When the file opens in text editor, add the line below under ‘[Desktop Entry]’ section and save it.
NoDisplay=true
After saving the file, the application will no longer visible in both app launcher (or Gnome ‘Show Apps’ screen) and search result. However, user can still right-click on associated file and use “Open With” dialog to find it.
Instead of using “NoDisplay=true“, you may use “Hidden=true” instead. So, not only for app launcher and search result, it’s also hidden from associated file’s “Open With” dialog.
(New) Method 2: Single command to hide app icon
For those who are familiar with Linux commands, a single command can add NoDisplay=true or Hidden=true to your app’s .desktop file.
1. First, find out the .desktop file.
Depends on your Linux Distribution, you may run command below to find any .desktop file’s name that contains keyboard fox (replace it to yours).
locate "*fox*desktop"
Or, list any file under /usr/share/applications, which has keyword fox (change to yours) in filename.
ls /usr/share/applications |grep fox
2. Use desktop-file-edit command to hide app icon.
Once you got the .desktop file for your application, run command:
sudo desktop-file-edit --set-key=NoDisplay --set-value=true /usr/share/applications/firefox.desktop
In command, skip sudo if the .desktop file is in your home sub-directory. Replace NoDisplay with Hidden as you want. and change /usr/share/applications/firefox.desktop to /path/to/yours_app.desktop
Method 3: Use Gnome Shell Extension
For Ubuntu 22.04, Ubuntu 22.10, Ubuntu 23.04, Fedora 36/37/38 Workstation, and Arch Linux with most recent GNOME Desktop, there’s an extension to make things easier.
- For Ubuntu 22.04 and higher, just search for and install ‘Extension Manger‘ from Ubuntu Software. Then, use the tool to search and install “App Hider” extension.
Install ‘App Finder’ extension using “Extension Manager” app - For Fedora & other Linux, just go to link below in web browser and use ON/OFF switch to install the extension.
- After installing the extension, click “Show Apps” (the 9 dots) icon in the dock launcher to show app grid. Finally, right-click on desired app icon and click “Hide” to hide it.
The extension by default only hide app icons from the app grid (click ‘Show Apps’ to activate). You can open its settings in either “Extension Manager” or “Gnome Extensions” app to configure to also hide from search result, or un-hide by removing items from list.